javascript A*算法实现最优路径规划
【代码】javascript A*算法实现最优路径规划。
·
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="800" height="800"></canvas>
<script>
// 创建二维数组来表示迷宫或地图,1代表障碍物,0代表可通过的空白格子
// const grid = [
// [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
// ];
var grid = [
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
];
// 绘制网格
// 绘制网格并填充颜色
function drawGrid(grid, path) {
const canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
const rows = grid.length;
const cols = grid[0].length;
const cellWidth = canvas.width / cols;
const cellHeight = canvas.height / rows;
// 绘制水平线和填充网格颜色
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
const x = j * cellWidth;
const y = i * cellHeight;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.rect(x, y, cellWidth, cellHeight);
if (grid[i][j] === 1) {
ctx.fillStyle = "black"; // 值为1的网格填充为黑色
} else {
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
ctx.strokeStyle = "black";
ctx.stroke();
}
// 根据路径二维数组填充蓝色
for (let k = 0; k < path.length; k++) {
if (path[k][0] === i && path[k][1] === j) {
ctx.fillStyle = "blue";
break;
}
}
ctx.fill();
}
}
}
// 定义节点类
class Node {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.g = 0; // 从起点到当前节点的实际成本
this.h = 0; // 从当前节点到目标节点的预计成本(启发函数)
this.f = 0; // f = g + h,总成本
this.parent = null; // 父节点,用于路径回溯
}
}
// A*算法路径规划函数
function astar(startX, startY, endX, endY, grid) {
const openList = []; // 开放列表,用于存储待考虑扩展的节点
const closedList = []; // 封闭列表,用于存储已经考虑过的节点
// 创建起点和目标节点
const startNode = new Node(startX, startY);
const endNode = new Node(endX, endY);
// 将起点添加到开放列表
openList.push(startNode);
// 计算启发函数(曼哈顿距离)
function heuristic(node) {
return Math.abs(node.x - endNode.x) + Math.abs(node.y - endNode.y);
}
// 判断节点是否在封闭列表中
function isInClosedList(x, y) {
for (let i = 0; i < closedList.length; i++) {
if (closedList[i].x === x && closedList[i].y === y) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 寻找最优路径
while (openList.length > 0) {
// 从开放列表中选择f值最小的节点作为当前节点
let currentNode = openList[0];
let currentIndex = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < openList.length; i++) {
if (openList[i].f < currentNode.f) {
currentNode = openList[i];
currentIndex = i;
}
}
// 将当前节点从开放列表移动到封闭列表
openList.splice(currentIndex, 1);
closedList.push(currentNode);
// 找到目标节点,路径规划完成
if (currentNode.x === endNode.x && currentNode.y === endNode.y) {
const path = [];
let current = currentNode;
while (current !== null) {
path.push([current.x, current.y]);
current = current.parent;
}
return path.reverse();
}
// 扩展当前节点的邻居节点
const neighbors = [{
x: 0,
y: -1
}, // 上
{
x: 0,
y: 1
}, // 下
{
x: -1,
y: 0
}, // 左
{
x: 1,
y: 0
} // 右
];
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) {
const neighborX = currentNode.x + neighbors[i].x;
const neighborY = currentNode.y + neighbors[i].y;
// 跳过超出边界或在封闭列表中的节点
if (
neighborX < 0 ||
neighborX >= grid.length ||
neighborY < 0 ||
neighborY >= grid[0].length ||
isInClosedList(neighborX, neighborY)
) {
continue;
}
// 跳过障碍物(1)
if (grid[neighborX][neighborY] === 1) {
continue;
}
// 创建邻居节点并计算成本
const neighborNode = new Node(neighborX, neighborY);
neighborNode.g = currentNode.g + 1; // 每个格子的实际成本均为1
neighborNode.h = heuristic(neighborNode);
neighborNode.f = neighborNode.g + neighborNode.h;
neighborNode.parent = currentNode;
// 如果邻居节点已经在开放列表中,则检查是否通过当前节点到达邻居节点的路径更优
let found = false;
for (let j = 0; j < openList.length; j++) {
if (
openList[j].x === neighborNode.x &&
openList[j].y === neighborNode.y
) {
found = true;
if (neighborNode.g < openList[j].g) {
openList[j].g = neighborNode.g;
openList[j].f = neighborNode.f;
openList[j].parent = currentNode;
}
break;
}
}
// 如果邻居节点不在开放列表中,则将其添加到开放列表
if (!found) {
openList.push(neighborNode);
}
}
}
// 没有找到路径,返回空数组表示失败
return [];
}
// 示例使用
const start = {
x: 3,
y: 2
};
const end = {
x: 7,
y: 10
};
const path = astar(start.x, start.y, end.x, end.y, grid);
console.log(path);
drawGrid(grid,path);
</script>
</body>
</html>
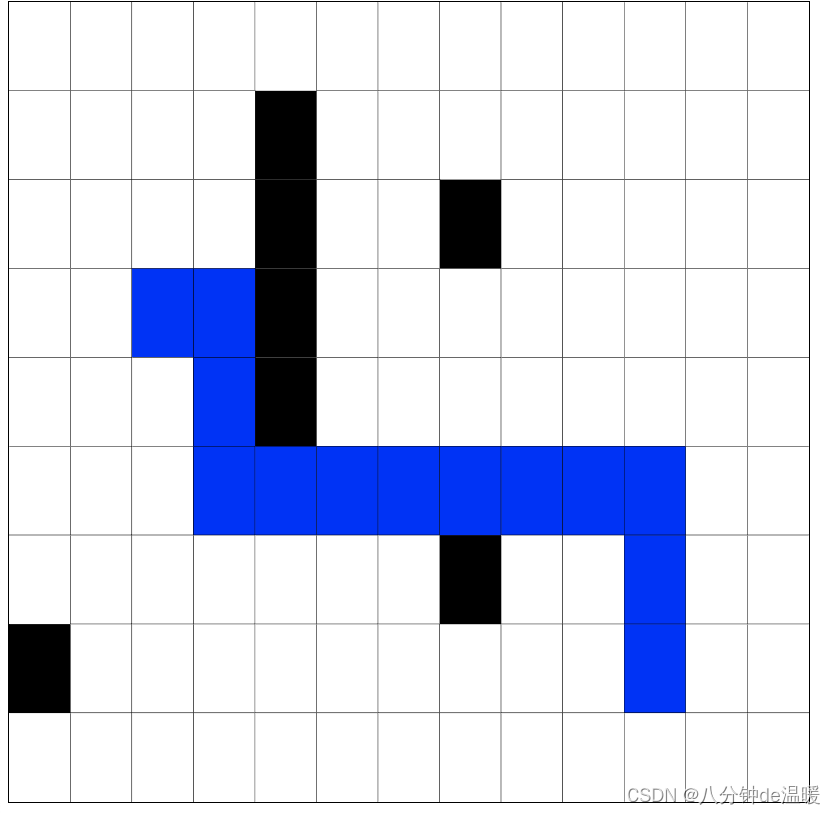
根据图片,生成障碍物二维数组,然后获取最优路径
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="800" height="800"></canvas>
<canvas id="canvas2" width="800" height="800"></canvas>
<script>
// 在Canvas中绘制图片
function drawImageOnCanvas(imagePath) {
const canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
const img = new Image();
img.src = imagePath;
const gridArray = [];
img.onload = function () {
canvas.width = img.width;
canvas.height = img.height;
ctx.drawImage(img, 0, 0); // 将图像绘制在Canvas的左上角(0, 0)处
const imageData = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
for (let i = 0; i < imageData.height; i++) {
const row = [];
for (let j = 0; j < imageData.width; j++) {
const index = (i * imageData.width + j) * 4;
const red = imageData.data[index];
const green = imageData.data[index + 1];
const blue = imageData.data[index + 2];
if (red === 0 && green === 0 && blue === 0) {
row.push(1); // 黑色像素点作为障碍物(1)
} else {
row.push(0); // 其他颜色的像素点为空白格子(0)
}
}
gridArray.push(row);
}
// 调用路径规划函数或其他处理逻辑
processGrid(gridArray);
};
}
// 绘制网格并填充颜色
function drawGrid(grid, path) {
console.log('grid: ', grid);
const canvas = document.getElementById("canvas2");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
const rows = grid.length;
const cols = grid[0].length;
const cellWidth = canvas.width / cols;
const cellHeight = canvas.height / rows;
// 绘制水平线和填充网格颜色
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
const x = j * cellWidth;
const y = i * cellHeight;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.rect(x, y, cellWidth, cellHeight);
if (grid[i][j] === 1) {
ctx.fillStyle = "black"; // 值为1的网格填充为黑色
} else {
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
ctx.strokeStyle = "white";
ctx.stroke();
}
// 根据路径二维数组填充蓝色
for (let k = 0; k < path.length; k++) {
if (path[k][0] === i && path[k][1] === j) {
ctx.fillStyle = "blue";
break;
}
}
ctx.fill();
}
}
}
// 定义节点类
class Node {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.g = 0; // 从起点到当前节点的实际成本
this.h = 0; // 从当前节点到目标节点的预计成本(启发函数)
this.f = 0; // f = g + h,总成本
this.parent = null; // 父节点,用于路径回溯
}
}
// A*算法路径规划函数
function astar(startX, startY, endX, endY, grid) {
const openList = []; // 开放列表,用于存储待考虑扩展的节点
const closedList = []; // 封闭列表,用于存储已经考虑过的节点
// 创建起点和目标节点
const startNode = new Node(startX, startY);
const endNode = new Node(endX, endY);
// 将起点添加到开放列表
openList.push(startNode);
// 计算启发函数(曼哈顿距离)
function heuristic(node) {
return Math.abs(node.x - endNode.x) + Math.abs(node.y - endNode.y);
}
// 判断节点是否在封闭列表中
function isInClosedList(x, y) {
for (let i = 0; i < closedList.length; i++) {
if (closedList[i].x === x && closedList[i].y === y) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 寻找最优路径
while (openList.length > 0) {
// 从开放列表中选择f值最小的节点作为当前节点
let currentNode = openList[0];
let currentIndex = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < openList.length; i++) {
if (openList[i].f < currentNode.f) {
currentNode = openList[i];
currentIndex = i;
}
}
// 将当前节点从开放列表移动到封闭列表
openList.splice(currentIndex, 1);
closedList.push(currentNode);
// 找到目标节点,路径规划完成
if (currentNode.x === endNode.x && currentNode.y === endNode.y) {
const path = [];
let current = currentNode;
while (current !== null) {
path.push([current.x, current.y]);
current = current.parent;
}
return path.reverse();
}
// 扩展当前节点的邻居节点
const neighbors = [{
x: 0,
y: -1
}, // 上
{
x: 0,
y: 1
}, // 下
{
x: -1,
y: 0
}, // 左
{
x: 1,
y: 0
} // 右
];
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) {
const neighborX = currentNode.x + neighbors[i].x;
const neighborY = currentNode.y + neighbors[i].y;
// 跳过超出边界或在封闭列表中的节点
if (
neighborX < 0 ||
neighborX >= grid.length ||
neighborY < 0 ||
neighborY >= grid[0].length ||
isInClosedList(neighborX, neighborY)
) {
continue;
}
// 跳过障碍物(1)
if (grid[neighborX][neighborY] === 1) {
continue;
}
// 创建邻居节点并计算成本
const neighborNode = new Node(neighborX, neighborY);
neighborNode.g = currentNode.g + 1; // 每个格子的实际成本均为1
neighborNode.h = heuristic(neighborNode);
neighborNode.f = neighborNode.g + neighborNode.h;
neighborNode.parent = currentNode;
// 如果邻居节点已经在开放列表中,则检查是否通过当前节点到达邻居节点的路径更优
let found = false;
for (let j = 0; j < openList.length; j++) {
if (
openList[j].x === neighborNode.x &&
openList[j].y === neighborNode.y
) {
found = true;
if (neighborNode.g < openList[j].g) {
openList[j].g = neighborNode.g;
openList[j].f = neighborNode.f;
openList[j].parent = currentNode;
}
break;
}
}
// 如果邻居节点不在开放列表中,则将其添加到开放列表
if (!found) {
openList.push(neighborNode);
}
}
}
// 没有找到路径,返回空数组表示失败
return [];
}
function processGrid(grid) {
// 示例使用
const start = {
x: 3,
y: 2
};
const end = {
x: 500,
y: 500
};
const path = astar(start.x, start.y, end.x, end.y, grid);
console.log(path);
drawGrid(grid, path);
}
// 主函数
function main() {
const imagePath = "./path1.png";
drawImageOnCanvas(imagePath);
}
main();
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="500" height="500"></canvas>
<script>
// 创建二维数组来表示迷宫或地图,1代表障碍物,0代表可通过的空白格子
// const grid = [
// [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
// [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
// ];
var grid = [
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //1
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //2
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //3
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //4
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //5
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //6
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //7
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //8
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //9
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //10
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //11
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //12
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //13
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //14
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], //15
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //16
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //17
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //18
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //19
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //20
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //21
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //22
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0], //23
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0], //24
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0], //25
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //26
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], //27
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0], //28
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0], //29
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0], //30
];
// 绘制网格
// 绘制网格并填充颜色
function drawGrid(grid, path) {
const canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
const rows = grid.length;
const cols = grid[0].length;
const cellWidth = canvas.width / cols;
const cellHeight = canvas.height / rows;
// 绘制水平线和填充网格颜色
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
const x = j * cellWidth;
const y = i * cellHeight;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.rect(x, y, cellWidth, cellHeight);
if (grid[i][j] === 1) {
ctx.fillStyle = "black"; // 值为1的网格填充为黑色
} else {
ctx.fillStyle = "white";
ctx.strokeStyle = "black";
// ctx.fillText(`(${parseInt(x)},${parseInt(y)})`, x, y);
ctx.stroke();
}
// 根据路径二维数组填充蓝色
for (let k = 0; k < path.length; k++) {
if (path[k][0] === i && path[k][1] === j) {
ctx.fillStyle = "blue";
break;
}
}
ctx.fill();
}
}
ctx.closePath();
if (path.length > 2) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.strokeStyle = 'green'; // 设置路径的颜色
ctx.lineWidth = 10;
ctx.lineJoin = "round";
for (let k = 0; k < path.length; k++) {
const x = path[k][1] * cellWidth + parseInt(cellWidth / 2);
const y = path[k][0] * cellHeight + parseInt(cellHeight / 2);
ctx.lineTo(x, y);
}
ctx.stroke();
ctx.closePath();
for (let k = 0; k < path.length; k++) {
ctx.beginPath();
const x = path[k][1] * cellWidth + parseInt(cellWidth / 2);
const y = path[k][0] * cellHeight + parseInt(cellHeight / 2);
if (k == 0) {
ctx.fillStyle = 'red'; // 设置路径的颜色
ctx.arc(x, y, 8, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fill();
}
if (k == path.length - 1) {
ctx.fillStyle = 'white'; // 设置路径的颜色
ctx.arc(x, y, 8, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.fill();
}
ctx.closePath();
}
}
}
// 定义节点类
class Node {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.g = 0; // 从起点到当前节点的实际成本
this.h = 0; // 从当前节点到目标节点的预计成本(启发函数)
this.f = 0; // f = g + h,总成本
this.parent = null; // 父节点,用于路径回溯
}
}
// A*算法路径规划函数
function astar(startX, startY, endX, endY, grid) {
const openList = []; // 开放列表,用于存储待考虑扩展的节点
const closedList = []; // 封闭列表,用于存储已经考虑过的节点
// 创建起点和目标节点
const startNode = new Node(startX, startY);
const endNode = new Node(endX, endY);
// 将起点添加到开放列表
openList.push(startNode);
// 计算启发函数(曼哈顿距离)
function heuristic(node) {
return Math.abs(node.x - endNode.x) + Math.abs(node.y - endNode.y);
}
// 判断节点是否在封闭列表中
function isInClosedList(x, y) {
for (let i = 0; i < closedList.length; i++) {
if (closedList[i].x === x && closedList[i].y === y) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 寻找最优路径
while (openList.length > 0) {
// 从开放列表中选择f值最小的节点作为当前节点
let currentNode = openList[0];
let currentIndex = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < openList.length; i++) {
if (openList[i].f < currentNode.f) {
currentNode = openList[i];
currentIndex = i;
}
}
// 将当前节点从开放列表移动到封闭列表
openList.splice(currentIndex, 1);
closedList.push(currentNode);
// 找到目标节点,路径规划完成
if (currentNode.x === endNode.x && currentNode.y === endNode.y) {
const path = [];
let current = currentNode;
while (current !== null) {
path.push([current.x, current.y]);
current = current.parent;
}
return path.reverse();
}
// 扩展当前节点的邻居节点
const neighbors = [{
x: 0,
y: -1
}, // 上
{
x: 0,
y: 1
}, // 下
{
x: -1,
y: 0
}, // 左
{
x: 1,
y: 0
} // 右
];
for (let i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) {
const neighborX = currentNode.x + neighbors[i].x;
const neighborY = currentNode.y + neighbors[i].y;
// 跳过超出边界或在封闭列表中的节点
if (
neighborX < 0 ||
neighborX >= grid.length ||
neighborY < 0 ||
neighborY >= grid[0].length ||
isInClosedList(neighborX, neighborY)
) {
continue;
}
// 跳过障碍物(1)
if (grid[neighborX][neighborY] === 1) {
continue;
}
// 创建邻居节点并计算成本
const neighborNode = new Node(neighborX, neighborY);
neighborNode.g = currentNode.g + 1; // 每个格子的实际成本均为1
neighborNode.h = heuristic(neighborNode);
neighborNode.f = neighborNode.g + neighborNode.h;
neighborNode.parent = currentNode;
// 如果邻居节点已经在开放列表中,则检查是否通过当前节点到达邻居节点的路径更优
let found = false;
for (let j = 0; j < openList.length; j++) {
if (
openList[j].x === neighborNode.x &&
openList[j].y === neighborNode.y
) {
found = true;
if (neighborNode.g < openList[j].g) {
openList[j].g = neighborNode.g;
openList[j].f = neighborNode.f;
openList[j].parent = currentNode;
}
break;
}
}
// 如果邻居节点不在开放列表中,则将其添加到开放列表
if (!found) {
openList.push(neighborNode);
}
}
}
// 没有找到路径,返回空数组表示失败
return [];
}
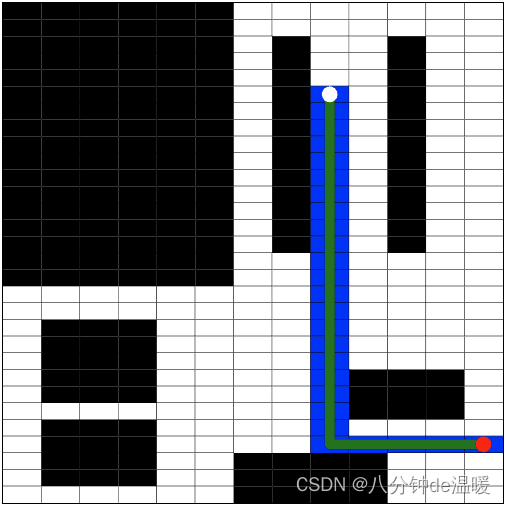
//x的范围为[0,29]
//y的范围为【0,12】
// 示例使用
// const start = {
// x: Math.floor(Math.random() * 30), //x是纵向
// y: Math.floor(Math.random() * 13) //y是横向
// };
// console.log('start: ', start);
// const end = {
// x: Math.floor(Math.random() * 30),
// y: Math.floor(Math.random() * 13)
// };
// console.log('end: ', end);
const start = {
x: 26, //x是纵向
y: 12 //y是横向
};
const end = {
x: 5,
y: 8
};
const path = astar(start.x, start.y, end.x, end.y, grid);
if (path.length == 0) {
path.push([start.x, start.y], [end.x, end.y])
}
console.log(path);
drawGrid(grid, path);
</script>
</body>
</html>
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)